Initial BBB configuration
Refer to bbb_setup.html for how to
configure the BBB for flashing.
The following shows how to connect clip to the BBB (on the P9 header), for SOIC-16 (clip: Pomona 5252):
POMONA 5252 (correlate with the BBB guide)
=== ethernet jack and VGA port ====
NC - - 21
1 - - 17
NC - - NC
NC - - NC
NC - - NC
NC - - NC
18 - - 3.3V (PSU)
22 - - NC - this is pin 1 on the flash chip
=== SATA port ===
This is how you will connect. Numbers refer to pin numbers on the BBB, on the plugs near the DC jack.

The following shows how to connect clip to the BBB (on the P9 header), for SOIC-8 (clip: Pomona 5250):
POMONA 5250 (correlate with the BBB guide)
=== RAM slots ====
18 - - 1
22 - - NC
NC - - 21
3.3V (PSU) - - 17 - this is pin 1 on the flash chip
=== slot where the AC jack is connected ===
This is how you will connect. Numbers refer to pin numbers on the BBB, on the plugs near the DC jack.

The procedure
Remove all screws:

It is also advisable to, throughout the disassembly,
place any screws and/or components that you removed in
the same layout or arrangement. The follow photos demonstrate
this:


Remove the HDD/SSD and optical drive:


Remove the palm rest:


Remove the keyboard and rear bezel:






If you have a WWAN/3G card and/or sim card reader,
remove them permanently. The WWAN-3G card has proprietary firmware inside; the technology is identical
to what is used in mobile phones, so it can also track
your movements:


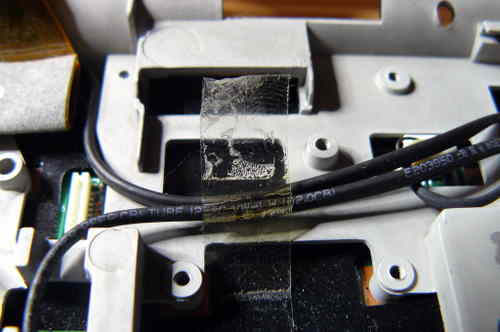
Remove this frame, and then remove the wifi chip:



Remove the speakers:







Remove the NVRAM battery (already removed in this photo):

When you re-assemble, you will be replacing the wifi chip
with another. These two screws don't hold anything together,
but they are included in your system because the screw
holes for half-height cards are a different size, so
use these if you will be installing a half-height card:

Unroute the antenna wires:




Disconnect the LCD cable from the motherboard:


Remove the LCD assembly hinge screws, and then remove the LCD
assembly:



Remove the fan and heatsink:



Remove this screw:

Remove these cables, keeping note of how and in what
arrangement they are connected:









Disconnect the power jack:


Remove the motherboard and cage from the base
(the marked hole is where those cables were routed through):


Remove all screws, arranging them in the same layout
when placing the screws on a surface and marking each screw
hole (this is to reduce the possibility of putting them
back in the wrong holes):


Also remove this:


Separate the motherboard from the cage:


The flash chip is next to the memory slots. On this
system, it was a SOIC-8 (4MiB or 32Mb) flash chip:

Connect your programmer, then connect GND and 3.3V





A dedicated 3.3V PSU was used to create this guide, but
at ATX PSU is also fine:

Of course, make sure to turn on your PSU:

Now, you should be ready to install libreboot.
Flashrom binaries for ARM (tested on a BBB) are distributed in libreboot_util. Alternatively,
libreboot also distributes flashrom source code which can be built.
Log in as root on your BBB, using the instructions in bbb_setup.html#bbb_access.
Test that flashrom works:
# ./flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev1.0,spispeed=512
In this case, the output was:
flashrom v0.9.7-r1854 on Linux 3.8.13-bone47 (armv7l)
flashrom is free software, get the source code at http://www.flashrom.org
Calibrating delay loop... OK.
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6405(D)" (8192 kB, SPI) on linux_spi.
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6406E/MX25L6436E" (8192 kB, SPI) on linux_spi.
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6445E/MX25L6473E" (8192 kB, SPI) on linux_spi.
Multiple flash chip definitions match the detected chip(s): "MX25L6405(D)", "MX25L6406E/MX25L6436E", "MX25L6445E/MX25L6473E"
Please specify which chip definition to use with the -c <chipname> option.
How to backup factory.rom (change the -c option as neeed, for your flash chip):
# ./flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev1.0,spispeed=512 -r factory.rom
# ./flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev1.0,spispeed=512 -r factory1.rom
# ./flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev1.0,spispeed=512 -r factory2.rom
Note: the -c option is not required in libreboot's patched flashrom, because
the redundant flash chip definitions in flashchips.c have been removed.
Now compare the 3 images:
# sha512sum factory*.rom
If the hashes match, then just copy one of them (the factory.rom) to a safe place (on a drive connected to another system, not
the BBB). This is useful for reverse engineering work, if there is a desirable behaviour in the original firmware
that could be replicated in coreboot and libreboot.
Follow the instructions at ../hcl/gm45_remove_me.html#ich9gen
to change the MAC address inside the libreboot ROM image, before flashing it.
Although there is a default MAC address inside the ROM image, this is not what you want. Make sure
to always change the MAC address to one that is correct for your system.
Now flash it:
# ./flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev1.0,spispeed=512 -w path/to/libreboot/rom/image.rom -V
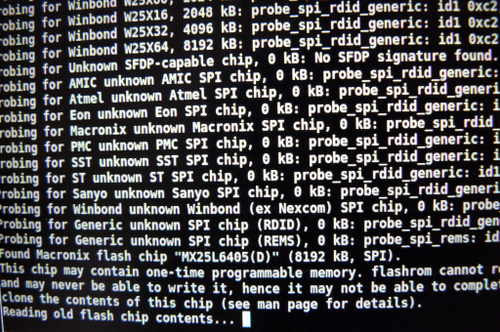
You might see errors, but if it says Verifying flash... VERIFIED at the end, then it's flashed and should boot.
If you see errors, try again (and again, and again); the message Chip content is identical to the requested image
is also an indication of a successful installation.
Example output from running the command (see above):
flashrom v0.9.7-r1854 on Linux 3.8.13-bone47 (armv7l)
flashrom is free software, get the source code at http://www.flashrom.org
Calibrating delay loop... OK.
Found Macronix flash chip "MX25L6405(D)" (8192 kB, SPI) on linux_spi.
Reading old flash chip contents... done.
Erasing and writing flash chip... FAILED at 0x00001000! Expected=0xff, Found=0x00, failed byte count from 0x00000000-0x0000ffff: 0xd716
ERASE FAILED!
Reading current flash chip contents... done. Looking for another erase function.
Erase/write done.
Verifying flash... VERIFIED.
Back to top of page.
Copyright © 2015 Leah Rowe <info@minifree.org>
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document
under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.3
or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation;
with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts.
A copy of the license can be found at ../gfdl-1.3.txt
Updated versions of the license (when available) can be found at
https://www.gnu.org/licenses/licenses.html
UNLESS OTHERWISE SEPARATELY UNDERTAKEN BY THE LICENSOR, TO THE
EXTENT POSSIBLE, THE LICENSOR OFFERS THE LICENSED MATERIAL AS-IS
AND AS-AVAILABLE, AND MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF
ANY KIND CONCERNING THE LICENSED MATERIAL, WHETHER EXPRESS,
IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHER. THIS INCLUDES, WITHOUT LIMITATION,
WARRANTIES OF TITLE, MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, ABSENCE OF LATENT OR OTHER DEFECTS,
ACCURACY, OR THE PRESENCE OR ABSENCE OF ERRORS, WHETHER OR NOT
KNOWN OR DISCOVERABLE. WHERE DISCLAIMERS OF WARRANTIES ARE NOT
ALLOWED IN FULL OR IN PART, THIS DISCLAIMER MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
TO THE EXTENT POSSIBLE, IN NO EVENT WILL THE LICENSOR BE LIABLE
TO YOU ON ANY LEGAL THEORY (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION,
NEGLIGENCE) OR OTHERWISE FOR ANY DIRECT, SPECIAL, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE, EXEMPLARY, OR OTHER LOSSES,
COSTS, EXPENSES, OR DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THIS PUBLIC LICENSE OR
USE OF THE LICENSED MATERIAL, EVEN IF THE LICENSOR HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH LOSSES, COSTS, EXPENSES, OR
DAMAGES. WHERE A LIMITATION OF LIABILITY IS NOT ALLOWED IN FULL OR
IN PART, THIS LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
The disclaimer of warranties and limitation of liability provided
above shall be interpreted in a manner that, to the extent
possible, most closely approximates an absolute disclaimer and
waiver of all liability.













































































